
by Julia Felton | Oct 10, 2023
In the fast-paced and ever-evolving landscape of today’s business world, a company’s success often hinges on the collective capabilities of its teams. As a business leader, you understand the importance of investing in your team’s growth and development. One essential aspect that should not be overlooked is Team Emotional Intelligence (Team EQ).
Team-level emotional intelligence, or Team EQ, refers to a group’s ability to interact harmoniously, both internally among team members and externally with individuals from other departments, teams, and even outside the organization. Teams that excel in Team EQ not only recognise unproductive emotions when they surface but also manage them constructively, paving the way to overcome interpersonal and inter-team challenges and achieve peak performance.
Research has shown that teams with strong EQ skills are more adept at navigating challenges, making effective decisions, and ultimately achieving peak performance. So, the question arises: How can you improve the performance of your team through Team Emotional Intelligence?
The case for team emotional intelligence
Teams are the backbone of any organisation, and they consist of individuals with varying levels of emotional intelligence. To unlock your team’s full potential, it’s imperative to provide them with opportunities to develop emotional intelligence skills collectively. Team EQ goes beyond individual emotional awareness; it involves the ability of team members to interact harmoniously within the group, across departments, and even outside the organization. Teams that excel in Team EQ can recognise and manage unproductive emotions constructively, surmount interpersonal and inter-team challenges, and achieve exceptional results.
Highly emotionally intelligent teams offer a plethora of benefits, including better decision-making, fostering a positive work environment, and increased adaptability to unforeseen changes such as virtual work environments, personnel shifts, shifting priorities, or intensified competition.
The 4 core team EQ skills
To harness the power of Team Emotional Intelligence effectively, it’s vital to understand the four core skills that make up a high EQ team:
- Emotion Awareness: Team members are attuned to their own emotions.
- Emotion Management: They can manage their emotions effectively.
- Internal Relationship Management: Positive working relationships are nurtured within the team.
- External Relationship Management: Team members can build relationships outside the team.
Team EQ skills in action
Consider the example of nursing teams, where high levels of Team EQ are paramount. Emotion awareness and management are crucial in high-stress, fast-paced environments where decisions can have life-altering consequences. Teams with strong internal relationship management can work cohesively and efficiently, supporting each other during extended shifts or demanding situations. External relationship management ensures compassionate care for patients and their families, leading to higher patient care ratings.
Components of team emotional intelligence
Team EQ serves as the foundation for a host of critical skills, including effective communication, empathy, and influence. Understanding and respecting teammates’ emotions enhance a team’s ability to work collaboratively and adapt swiftly to change.
From insights to action
Perhaps the most encouraging insight from EQ research is that Team EQ skills can be developed over time. This means that teams that initially score low in Team EQ can make significant improvements within six months to a year with dedicated practice. This holds true across professions and industries, making it a universally applicable concept.
As a business leader, investing in your team’s emotional intelligence is an investment in your organisation’s success. By nurturing Team Emotional Intelligence, you empower your teams to overcome challenges, foster positive working environments, and adapt gracefully to the ever-changing business landscape.
The result? Improved team performance and a brighter future for your company.
by Julia Felton | Sep 12, 2023
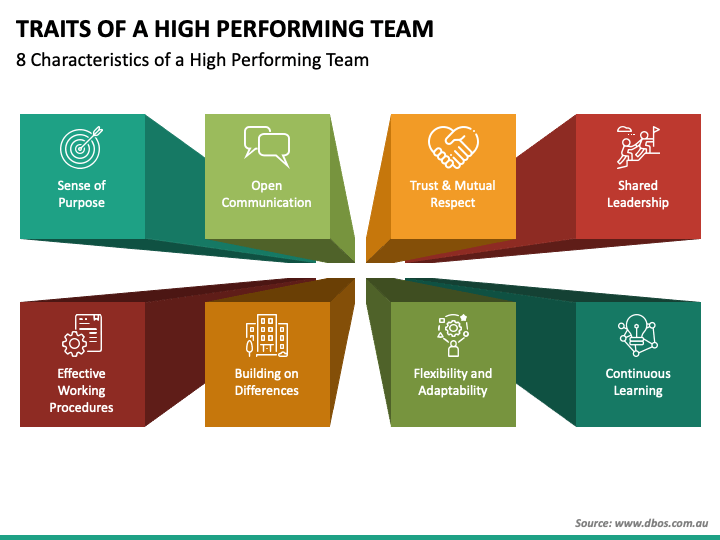
The three psychological needs essential in a high-performing team are autonomy, competence, and relatedness.
Of these, relatedness, or the desire to feel connected to others, has always been the trickiest for organisations to cultivate. It’s one thing to attract talented employees — but how exactly do you get them to like each other? When people feel psychologically fulfilled, they tend to be healthier, happier, and more productive.
Here are the 8 characteristics of a high-performing team with strong ‘relatedness’
- Sense of Purpose:
Individuals with a sense of purpose have clearly defined their mission and goals since the beginning. These people have set their eyes on the priorities and are driven with a strong focus on results and solution.
- Open Communication:
One of the most important characteristics of a high-performing team is open communication. Members who are not afraid to express their ideas and thoughts, as well as listen to what others have to say, are indeed professionals.
- Trust and Mutual Respect:
Respect and trust are two words that correlate with each other. In a professional setting, a leader and its followers do exist. As part of a team, both should learn how to trust and respect each other.
- Shared Leadership:
An effective leader asks for ideas and suggestions from their members. They value their team’s insights and are not autocratic. This kind of leader understands the key role of their members.
- Effective Working Procedures:
Aside from being highly skilled, effective team leaders are also resourceful. They don’t stop at “good” but rather aim for the “best”, every chance they get. They encourage creativity and find the most outstanding way to achieve their goal.
- Building on Differences:
Efficient leaders don’t look at differences as drawbacks of an individual. Instead, they use it as a weapon to create alternatives and other approaches that may be useful in different situations.
- Flexibility and Adaptability:
A high-performing team consists of adaptable and agile individuals. Variables like a fast-paced working environment don’t scare these kinds of people for they can easily adjust to any given situation.
- Continuous Learning:
The hunger for discoveries and newly acquired knowledge is the last characteristic of a high-performing team. Their desire to learn everything that they can or what might help improve their craft is an essential matter.
A great way to help team members understand their relatedness to others is to help them appreciate the value and contribution they make to any team. We do this by measuring their energy for impact using the GC Index.

by Julia Felton | Aug 31, 2023
Increasingly business leaders are realizing that if they are to thrive in today’s volatile, uncertain, chaotic, and volatile (VUCA) economy they need to fully embrace the power of collaboration. The old models of command and control leadership fuelled by competition are simply not sustainable business models in a world where uncertainty dominates everything we do.
What is Collaboration?
The Cambridge Dictionary defines collaboration as “to work with someone else for a special purpose”. And it typically involves two or more people, teams, or organizations combining their resources to achieve the goal. It is a win-win situation where the sum of the parts ends up being more than the whole. One party contributes something that is built on and then leveraged by the other party. The end result is something much better than any of the parties could have achieved individually.
However, in my experience, many people think collaboration means one person or entity has to relinquish something to make the collaboration work. This would be an example of a win-lose relationship and that is not what we are striving for here.
Collaborative Examples In Nature
Nature understands how collaboration works and there are many examples that we can see around us. A few include:
- Ants and bees working in collaboration and in collective ways to establish their hives and colonies
- Sea anemones and clownfish cultivate cooperative relationships with each other to provide protection and nutrients
- Water buffalo have a symbiotic, collaborative relationship with egrets. The egrets pick parasites out of the water buffalo’s skin, which in turn provide a source of nourishment for them. They also provide a warning system of any impending danger for the water buffalo
One of the reasons why nature values collaboration is because it understands and appreciates the inter-dependence and inter-connectedness of everything. Nothing happens in isolation in nature. Everything has an impact on something else, which is a principle that many of us have not yet grasped. Because the reality of the situation is that everything that I do ultimately impacts and influences you in some way. You might not see the direct impact right now, but trust me it will. This is because everything in the world is comprised of energy and so each of us creates an impact ripple that expands either positively or negatively.
Collaborative Leadership
Collaborative principles can be applied to all areas of business including leadership. Long gone are the days when anyone leader can know everything there is to know. That is simply not possible in this Information Age where leaders are inundated with information. We are literally drowning it in.
A New York Times Weekly edition contains more information than the average person in the seventeenth century would have come across in their entire lifetime. In 2008 we consumed three times as much information as in 1960, and by 2020 it is estimated that we generated 44 times more data than we produced in 2015. This is why smart leaders are now embracing the concept of collaboration in leadership through a process called Shared Leadership.
Shared Leadership occurs when two or more people decide to work collaboratively together to lead the team or project. The benefit of this approach is that the “best” leader can step up and lead at the most appropriate time. For example, some leaders provide the best ideas when a project is just starting out; other leaders are better at setting and maintaining the direction; others are great at rallying the team and getting others on board; whilst other leaders are better at implementing and getting things done; finally others are better at refining and improving the product or service. Imagine how much more effective the leadership could be in your business if multiple people collaborated in the shared leadership process.
A fabulous model of how to embrace Shared Leadership exists in nature and specifically in herds of wild horses. They utilize the Diamond Model of Leadership as a way to collaborate and share leadership, using three different leadership positions.
- Leading from the front
- Leading from the back
- Leading from the middle
The lead mare sets the direction and pace of the herd from the front of the diamond formation. She pays attention to what is happening in the environment and then makes a decision on where to go next. The lead stallion keeps the herd together and protects it from predators and is positioned at the back of the diamond. He influences the energy at which the herd moves. The rest of the herd, the sentinels, cover the other two points of the diamond, and lead from the middle, covering the outer sides of the diamond. Their role is to align the herd in the direction that has been set and detect potential threats coming from the side In addition to responding to threats, the sentinels are often the ambassadors of the herd and are the first to welcome new members.
The ever-present goal of herd leadership is health, harmony, and unity. With the unpredictability that nature ensures, herd leaders are often presented with challenges that require them to either reposition themselves to respond to changes in the environment or possibly even change roles to leverage their strengths differently. For example, when a threat emerges, like the new presence of a stranger or predator, the sentinel will often move from the center of the herd to the front where the threat appears. The sentinel will often redirect the herd away from danger. Once the lead mare senses the direction to safety, she will emerge back in front of the herd to set the new course. Once safe movement begins, the sentinel will return to the centre position.
Collaborative leadership has enabled horse herds to exist for over 50 million years as they have learnt to adapt and evolve to thrive in the uncertain environments they have experienced.
I’d love to hear from you about other collaborative relationships you’ve seen in nature and how you can apply these to your business.

by Julia Felton | Jul 3, 2023
Teamwork is paramount to the success of any business and leaders need to understand that without every team member pulling together in the same direction (aka with the same purpose) then success is likely to be curtailed, maybe not in the short term but definitely over the longer term.
Whilst individuals play the game it is teams that win championships whether that is in the sports arena or on the business playing field. Teamwork remains the ultimate competitive advantage in business today, because it is so powerful and rare.
“Not Finance. Not Strategy. Not Technology. It is teamwork that remains the ultimate competitive advantage, both because it is so powerful and so rare” ‒ Patrick Lencioni
There are several benefits of being in a team and these include:
- Teams involve more people and therefore comprise more resources – time, ideas and energy – available than one individual would have
- Teams allow the leaders to maximise their potential and minimise their weaknesses
- Teams provide multiple perspectives on how to reach the goal, as each individual will see the problem in a different light. This allows for a creative flow of ideas, and the stumbling blocks that no one person might see can easily be navigated
- Teams share the credit for victories and the blame for losses. This fosters genuine humility and authentic communication
- Teams help keep leaders accountable for the goals
- Teams can simply do more than the individual
So why do business leaders fail to harness their teams for success and what are some of the myths we believe about teams. I believe there are five myths that keep many leaders stuck, not operating effectively.
Myth One: Teams are harmonious groups of people who compromise their needs for the sake of the group
Reality One: Good teams are made up of a diverse group of people with different perspectives and needs. When this diversity is recognised and embraced it becomes a real strength that can help the team overcome roadblocks that might derail a project.
So with this in mind it is important that within the team we identify the range of talents of all the team members and help team members understand the impact and contribution they can give to the team. Only then will team members feel engaged and motivated and want to actively participate.
Myth Two: Team conflict is unhealthy
Reality Two: Conflict can be healthy and should be harnessed for the common good, rather than suppressed.
Conflict is an energy source that when directed towards the team’s primary goal or mission can help create momentum and actually move a project forward. The challenge comes from the fact that many people dislike conflict and so suppress it. This creates frustration and a negative build-up of energy that ultimately can derail a project. Better the conflicting energy is surfaced and channelled in a positive way to come up with new ideas and approaches that help drive the project forward rather than derail it
Myth Three: Most people like teamwork
Reality Three: Whilst we often think that people enjoy working in teams, after all humans are social animals and we enjoy interaction with others, research by the Wright Consultancy discovered that only 33% of the working population enjoyed teamwork, 33% of the working population preferred working alone and solo, whilst the remaining 33% were pretty neutral as to their stance.
The challenge then for leaders is to know the drivers of the people in their teams and their preferred working style and then create roles that best leverage that person’s skills and method of working
Myth Four: Teams are easy to influence and manage
Reality Four: Leading and managing teams requires a different set of skills from that required for day-to-day management. This is because when you are leading teams you need to be able to inspire and motivate others. Also, you need to practice and understand the difference between delegation and empowerment, as teams work best when given direction and then allowed to decide how to reach that goal themselves. Micro-management hampers engagement and stops innovation as team members need to feel that the leader has their back and trusts them implicitly to do the job
Myth Five: Senior Leaders encourage teamwork
Reality Five: Most leaders are anxious about teamwork and the potential loss of power or control
A study of European managers in the 1990’s discovered that whilst senior leaders outwardly encouraged teamwork internally they were uncomfortable with the process and the potential for it exposing their own weaknesses and loss of control. This then often results in office politics with one team withholding resources from another in order to exert their authority.
Much of this thinking is driven by fear because great leaders realise they always need to hire people better than themselves so that their weaknesses can be mitigated for the ongoing success of the business. When leaders realise that it is results that matter and not their ego, they become more collaborative and work together across various aspects of the business to achieve success.
Nature understands the importance of teamwork and how everything is interdependent and synergistic. This is what drives unity and harmony in nature. So perhaps there is something we can learn from it and apply to our own efforts at improving teamwork, because as in the words of Simon Mainwaring
“Creating a better world requires teamwork, partnerships and collaboration, as we need an entire army of companies to work together to build a better world within the next few decades. This means corporations must embrace the benefit of co-operating with one another”

by Julia Felton | Aug 4, 2022
One thing that I think we can all agree on is that the last two years have changed forever the way we live and work. As much as people talk about things returning to normal after the COVID pandemic, in my opinion, they never will. Too many parameters have changed, people’s mindsets and behaviours have changed, our business processes and systems have changed, and in many cases, our entire product offering has changed and adapted to meet the ever-changing needs of our clients.
Very importantly the dynamics of our teams have changed and leaders need to become very aware of this. Leaders cannot assume that things will revert to how they were, and whilst for some leaders this might prove to be challenging, many leaders I am speaking with are excited about this opportunity which allows them to reframe how their teams operate.
Leaders have the opportunity to reinvent their teams and businesses; to start afresh rather than returning to the unhelpful behaviours and out of date approaches they once used. But what exactly is reinvention and how does it differ from change?
When you look up the term reinvention in the dictionary it says: “the action or process through which something is changed so much that it appears to be entirely new” and this contrasts with change which is defined as “to make (someone or something) different; alter or modify”.
So in essence reinvention could be defined as a radical change to creates something entirely new. Athos, Goss, Pascale in an article in the Harvard Business Review: The Reinvention Roller Coaster: Risking the Present for a Powerful Future provides the following definition:
“Reinvention is not changing what is, but creating what isn’t. A butterfly is not more caterpillar or a better or improved caterpillar; a butterfly is a different creature. Incremental change isn’t enough for many companies today. They don’t need to change what is; they need to create what isn’t.” –
For which Athos, Goss and Pascale add, “When a company reinvents itself, it must alter the underlying assumptions and invisible premises on which its decisions and actions are based. To reinvent itself, an organisation must first uncover its hidden context. Only when an organisation is threatened, losing momentum, or eager to break new ground will it conform its past and begin to understand why it must break with its outmoded present. And only then will a company’s employees come to believe in a powerful new future, a future that may seem beyond the organisation’s reach.”
Reinvention Mindsets
What is interesting for me is the different mindsets that are involved in change versus reinvention. As individuals and organisations we often continuously push back and resist change; even when we understand that change is an ongoing necessity if we are going to effectively adapt and sustain any form of continued relevance in moving forward into the future.
There are a variety of reasons as to why leaders and team members resist change and these include:
- an unwillingness to part ways with or release strategies that have led to previous success,
- lack of trust and/or relationship,
- lack of understanding or clarity in the communication of the change,
- a possible loss of individual or organisational status or hierarchy,
- lack of capacity to effectively implement the change,
- fear of the unknown, uncertainty, or failure that can accompany a change.
All of these factors must be understood and addressed if any change initiative is to take hold.
And while change is a natural, but not necessarily comfortable process, individual or organisational transformation or reinvention is not.
Re-invention requires a different mindset, a completely different level of capacity, and a very different way of considering the future, which requires new behaviours that necessitate new ways of thinking, doing, acting and being.
Just consider the massive re-invention we have seen in the hospitality industry over the last few years. Who would have ever thought that fine dining restaurants would start offering take-away service? But they have, partly out of necessity during the height of the pandemic to survive and also to meet their customer needs, and many are continuing to provide this service and in doing so have created a new revenue stream.
So, as you bring your team back together consider how can you start the re-invention process. What can you do to help the team transform and emerge stronger than before? What new practices need to be instigated? What new mindsets and behaviours need to be adopted?
Teams that succeed will initiate and embed new and exciting approaches of working together that enable them to adapt and respond to the future environment which will, in turn, lead to:
- increased cohesiveness in the face of increased complexity and pace of execution
- better collective decision making and goals
- clarity about agile ways of working that lead to success
- focus on the key priorities to drive results
- improved communication, trust and commitment to each other.
Please share what you are doing to reinvent your team and business and why not take the Unbridled Business Assessment to help you identify the key business areas that must be aligned for you to reinvent your business so you can lead it through uncertainty

by Julia Felton | May 3, 2022
3 May 2022, Yorkshire, UK. – Julia Felton believes in a world where rather than humanity solving the problems of nature, nature can solve the problems of humanity. She believes that there exists in nature a blueprint for a better way to live and lead businesses and she presents these findings in her latest book, Unbridled Business: Unlocking Nature’s Wisdom To Reinvent Leadership.
There is no doubt that the events of the past two years have changed everything. Even before the pandemic business needed to change but recent events have accelerated this. No longer do businesses simply need to change, they need to reinvent if they are to become agile and adaptable to navigate the uncertainty in which we now live.
We now have the opportunity to shed all the old work practices that no longer serve us and start afresh.
The challenge is that up to now there hasn’t existed a blueprint on how to do this. How do we move from the command and control leadership structures designed for the industrial age to a leadership style based on connection, collaboration and community?
Julia discovered that a solution lies in nature and herds of horses. After all, they have navigated change and survived for millions of years. In Unbridled Business, she codifies this solution into the Unbridled Business BlueprintÔ that can be used to help business leaders reinvent their business so that it is fit for purpose for the 21st century.
It all starts with Embedding The Purpose into everything you all and then Evolving The Leadership, Empowering Others To Act and Engaging The Environment and the result is Unbridled Performance. A business that can create real impact whilst delivering increased productivity, profitability and team engagement.
Why look to nature and herds of horses?
1) Adaptability – Horses have existed on the planet for over 50 million years, whilst humans have only lived here for 6 million years. They have learnt how to become agile and adapt to changing situations to survive.
2) Leading Through Uncertainty – There exists in herds of horses a model to help us lead through the uncertainty, that this VUCA world presents. It’s based on the premise of four simple steps – The Diamond Model of Leadership.
3) Shared Leadership – In this attention vying world there is simply no way that one person (typically the leader) can know everything. Now more than ever there is a need for Shared Leadership, with the best person stepping forward at the right time.
One of the biggest awakening moments for humanity from the Pandemic is that we are all inter-dependent and inter-connected. We all impact each other whether we are consciously aware of it or not. Nature has always understood the power of inter-dependency as everything works as a system in harmony together, and when something falls out of balance nature self-regulates itself to correct that imbalance. Nature understands the importance of the collective “we” rather than the “me” model of being that is so prevalent in society today.
These are all themes that Julia has addressed in her latest book Unbridled Business – Unlocking Nature’s Wisdom To Reinvent Leadership due for release 3rd May.
To book Julia for an interview today, please contact her:
Phone: +44 7710 124848
Email: connect@businesshorsepower.com
Website: www.businesshorsepower.com
Follow Her on Social Media:
www.linkedin.com/in/juliafelton
www.facebook.com/juliamfelton
www.twitter.com/julia_felton

by Julia Felton | Jun 27, 2021
In this podcast, Julia and Andrew turn their thinking towards purpose. What is purpose and how has this changed with the impact of Covid-19. The discussion was sparked by a McKinsey quarterly article about purpose shifting from why to how. Julia was really inspired by this article, because she has been talking for a long time about purpose, and why it’s important for companies to have purpose, and we often talk about purpose before profits people have started to reevaluate what their own personal purpose is, and how they want to contribute to society.
Business is a force for good. But the more that organisations can get clear on their purpose, and collectively with their team members get clear on the purpose of the business, I think it absolutely gives people that NorthStar, you know people know where they’re going. And that gives them the safety and security and certainty that many of us have been lacking over the last few months.
The duo also touch on the impact of Covid-19 on the corporate social responsibility agenda. Andrew talks about the recent documentary on the planet with Prince William and how young people are changing their attitudes. They delve into John Mackey, Conscious Leadership to look at purpose along with Simon Sinek’s The Infinite Game where he clearly sets out the difference between a finite and an infinite mindset. They then discuss companies that practice what they preach.
Purpose is about that beating heart in the organisation, pushing blood and oxygen, that excitement, that infectiousness that it talks about in a positive infectiousness around the organisation. It is about creating win-win situations by getting your teams galvanized behind your purpose.
Show Notes:
Here are the highlights from this episode
- 00:46 McKinsey Quarterly: Purpose: Shifting from why to how April 2020
- https://www.mckinsey.com/business-functions/organization/our-insights/purpose-shifting-from-why-to-how#
- 01:44 Why it is important to have purpose
- 03:47 It’s more than just ticking boxes it is about hard wiring it into the DNA of a business.
- 04:33 A few years ago, Unilever came up what they called a massive transformational purpose for each of their different brands. And the brands that are totally have fully embraced this.
- 05:21 Ethical and moral dilemmas related to Covid-19 volunteering
- 07:00 How young people are changing attitudes.
- 10:25 the significance of what it means to write about issues in company reports
- 12:36 Conscious Leadership John Mackey
- 13:35 The Infinite Game Simon Sinek
- 13:56 https://www.zappos.com/
- 19:44 ”… when stakeholders so for stakeholders, we could read customers, employee shareholders anyone participate in and help evolve an organization’s higher purpose, it can be infectious. The whole company receives an extra boost of alignment. There are a few things More powerful than a shared commitment to a higher purpose among all relevant stakeholders, this allows everyone to feel connected to the beating heart of the organisation, at least to some degree…” Conscious Leadership John Mackey.
- 23:00 “When stakeholders see important decisions being made in ways that are aligned with the company’s core values. And when they see leaders actually engaged with that higher purpose. It has enormous impact, for lack of a better word, it gives people faith.” Conscious Leadership John Mackey

by Julia Felton | Apr 15, 2021
With the backdrop of a COVID pandemic Julia and Andrew tackle leadership and discuss various models linked to the herd.
There’s a real need for leaders to be agile and flexible. So what does that mean to Julia and Andrew? We find out through a canter looking at how the herd operates and challenging old styles of leadership
During the discussion the pair draw a direct link between how good our leaders are and their ability to navigate the current situation, inspire and motivate others and the results of the company. Finding a direct linear connection and empirical evidence of how if we’ve got better leaders, we can actually improve team performance and get better results.
The couple touch on the importance of and learning and development because there is a point at which leadership, when we’re looking at leadership, those that are planning and looking at how things are run, do need to have more of a commercial mind about them.
In essence we are all leaders, but what could shared leadership look like in an organisation and what can we learn from the herd?
Julia sets out how the mare leads at the front and the stallion at the back but what happens at the side this leads to dialogue on collaboration and the importance of empowering your teams. To round off the conversation Julia and Andrew look at the impact on millennials
Show Notes:
Here are the highlights from this episode
- 01:00 The need to develop better leaders
- 01:42 Is leadership a soft skill?
- 01:52 The concept of shared leadership
- 02:47 Comparing the old styles of leadership
- 04:40 What is shared leadership and how do we learn from the herd?
- 05:05 It’s about leading from the front
- 05:34 Pull / push energy
- 06:45 Channeling energy
- 07:00 Who is leading and who is providing energy from the back?
- 09:00Leading from the side
- 10:13 Being a herd member means you are still a leader
- 10:57 The power of empowerment
- 11:50 Accountability
- 12:54 It’s back to nature
- 13:57 Deloitte Human Capital Survey 2020
- 16:35 Jim Collins the importance of talent

by Julia Felton | Mar 4, 2021
In this episode Julia and Andrew look at to re-engage your teams as they start to return to work after furlough or a long period of home working.
Julia introduces a seven step pyramid model on how to start the process of rebuilding relationships based on what she learned from a horse trainer in America. The trainer observed horse rituals at a waterholes and how the horses interacted with each other to build relationships within the herd.
Horses are good at hanging out together doing something and doing nothing. And in the workplace, when we were actually physically in the workplace, the doing nothing would be the bit for Julia and Andrew, which is the water cooler talk, when we were hanging out. They pick up on the importance of reestablishing and developing good connections.
Andrew picks up on the importance of being self-aware about oneself and others and putting yourself into other people’s shoes and introduces a technique called Johari’s Window created by two American professors, Joe Luft and Harry Ingham, in the 1950s. So how do we press the connection reset button? What should we all be thinking about? It includes getting our body language right and knowing our own personal stories and how to use them in the reconnecting
Show Notes:
Here are the highlights from this episode
- 00:48 How do we get back to re-engaging in the workplace.
- 01:20 Waterhole rituals and the human water cooler conversations
- 01:48 Horses are good at hanging out together doing something and doing nothing
- 03:10 The magic of relationships comes in that time when we just hang out.
- 04:55 The importance of the self-awareness dial
- 06:10 Johari’s Window – devised in the 1950s by and they were two psychology professors in California.

by Julia Felton | Mar 1, 2021
The importance of agility and being agile and flexible in a fast moving world is explored in this episode of Impactful the Podcast, especially with the threat of potential and UK-wide local lockdowns.
The Impactful duo look at the problems with a rigid working practices and what we can learn from the recent national lockdown. Julia and Andrew look at structure relating it to a pendulum swinging between structure and no structure and what that shows us in terms of fluidity, freedom and security. They bring in their personal experiences to highlight how we can adapt to build momentum.
Julia discusses a piece of research that Accenture did on leadership imperatives for an agile business and its three pillars here, of what is called demystifying leadership and what we can learn from high performance leaders. Now we’re all coming back to work and everyone’s got very different agendas about how they want to return it comes down to different levels of flexibility and agility to respond to what’s going on and which is very, very different.
Can businesses be agile and flexible? Andrew talks about the importance of communication especially internally and the two then chat about employee engagement with reference to Robert Dilts logical levels of change, looking at environment behaviours, capabilities, beliefs, identity, identity, and purpose.
Show Notes:
Here are the highlights from this episode
- 01:54 Importance of transferable skills in the workplace
- 02:39 Are there barriers?
- 03:07 Structures operating like a pendulum
- 03:22 Structure gives freedom
- 03:40 Structure security
- 04:47 Proactive & Reactive – learning from the herd
- 09:15 Accenture Report – The Three Pillars
- 09:58 Pulling in the same direction
- 10:55 Shared Consensus
- 11:18 Talent & Skills
- 13:05 Employee engagement and internal comms
- 14:28 The Comfort zone
- 16:12 Trust as a leader
- 16:56 Robert Dilts – Logical Levels of Change















